Kevin MacDonald’s The Culture of Critique: A Provocative Analysis of the Causes of White Decline
Stanley Hornbeck, American Renaissance, March 1999
The Culture of Critique: An Evolutionary Analysis of Jewish Involvement in Twentieth-Century Intellectual and Political Movements, Kevin MacDonald, Praeger, 1998, 379 pp.
In The Culture of Critique, Kevin MacDonald advances a carefully researched but extremely controversial thesis: that certain 20th century intellectual movements — largely established and led by Jews — have changed European societies in fundamental ways and destroyed the confidence of Western man. He claims that these movements were designed, consciously or unconsciously, to advance Jewish interests even though they were presented to non-Jews as universalistic and even utopian. He concludes that the increasing dominance of these ideas has had profound political and social consequences that benefited Jews but caused great harm to gentile societies. This analysis, which he makes with considerable force, is an unusual indictment of a people generally thought to be more sinned against than sinning.

The Culture of Critique is the final title in Prof. MacDonald’s massive, three-volume study of Jews and their role in history. The two previous volumes are A People That Shall Dwell Alone and Separation and its Discontents, published by Praeger in 1994 and 1998. The series is written from a sociobiological perspective that views Judaism as a unique survival strategy that helps Jews compete with other ethnic groups. Prof. MacDonald, who is a psychologist at the University of California at Long Beach, explains this perspective in the first volume, which describes Jews as having a very powerful sense of uniqueness that has kept them socially and genetically separate from other peoples. The second volume traces the history of Jewish-gentile relations, and finds the causes of anti-Semitism primarily in the almost invariable commercial and intellectual dominance of gentile societies by Jews and in their refusal to assimilate. The Culture of Critique brings his analysis into the present century, with an account of the Jewish role in the radical critique of traditional culture.
The intellectual movements Prof. MacDonald discusses in this volume are Marxism, Freudian psychoanalysis, the Frankfurt school of sociology, and Boasian anthropology. Perhaps most relevant from a racial perspective, he also traces the role of Jews in promoting multiculturalism and Third World immigration. Throughout his analysis Prof. MacDonald reiterates his view that Jews have promoted these movements as Jews and in the interests of Jews, though they have often tried to give the impression that they had no distinctive interests of their own. Therefore Prof. MacDonald’s most profound charge against Jews is not ethnocentrism but dishonesty — that while claiming to be working for the good of mankind they have often worked for their own good and to the detriment of others. While attempting to promote the brotherhood of man by dissolving the ethnic identification of gentiles, Jews have maintained precisely the kind of intense group solidarity they decry as immoral among others.
Celebrating Diversity

Prof. MacDonald claims that one of the most consistent ways in which Jews have advanced their interests has been to promote pluralism and diversity — but only for others. Ever since the 19th century, they have led movements that tried to discredit the traditional foundations of gentile society: patriotism, racial loyalty, the Christian basis for morality, social homogeneity, and sexual restraint. At the same time, within their own communities and with regard to the state of Israel, they have often supported the very institutions they attack in gentile society.
Why is this in the interest of Jews? Because the parochial group loyalty characteristic of Jews attracts far less attention in a society that does not have a cohesive racial and cultural core. The Jewish determination not to assimilate fully, which accounts for their survival as a people for thousands of years — even without a country — has invariably attracted unpleasant and even murderous scrutiny in nations with well-defined national identities. In Prof. MacDonald’s view it is therefore in the interest of Jews to dilute and weaken the identity of any people among whom they live. Jewish identity can flower in safety only when gentile identity is weak.
Prof. MacDonald quotes a remarkable passage from Charles Silberman:
American Jews are committed to cultural tolerance because of their belief — one firmly rooted in history — that Jews are safe only in a society acceptant of a wide range of attitudes and behaviors, as well as a diversity of religious and ethnic groups. It is this belief, for example, not approval of homosexuality, that leads an overwhelming majority of American Jews to endorse ‘gay rights’ and to take a liberal stance on most other so-called ‘social’ issues.
He is saying, in effect, that when Jews make the diversity-is-our-strength argument it is in support of their real goal of diluting a society’s homogeneity so that Jews will feel safe. They are couching a Jewish agenda in terms they think gentiles will accept. Likewise, as the second part of the Silberman quotation suggests, Jews may support deviant movements, not because they think it is good for the country but because they think it is good for Jews.
Prof. Silberman also provides an illuminating quote from a Jewish economist who thought that Republicans had more sensible economic policies but who voted for the Democratic presidential candidate anyway. His reason? “I’d rather live in a country governed by the faces I saw at the Democratic convention than by those I saw at the Republican convention.” This man apparently distrusts white gentiles and voted for a racially mixed party even if its economic policies were wrong. What is good for Jews appears to come before what is good for the country.
Earl Raab, former president of heavily Jewish Brandeis University makes the diversity argument in a slightly different way. Expressing his satisfaction with the prediction that by the middle of the next century whites will become a minority, he writes,”We have tipped beyond the point where a Nazi-Aryan party will be able to prevail in this country.” He is apparently prepared to displace the people and culture of the founding stock in order to prevent the theoretical rise of an anti-Jewish regime. Prof. Raab appears to see whites mainly as potential Nazis, and is willing to sacrifice their cultural and national continuity in order to defuse an imagined threat to Jews. This passage takes for granted the continued future existence of Jews as a distinct community even as gentile whites decline in numbers and influence.
In the same passage, Prof. Raab continues by noting that, “[w]e [Jews] have been nourishing the American climate of opposition to bigotry for about half a century. That climate has not yet been perfected, but the heterogeneous nature of our population tends to make it irreversible . . .” — just as it tends to make the ultimate displacement of European culture also irreversible.
Prof. MacDonald traces the development of this diversity strategy to several sources. It is widely recognized that the German-Jewish immigrant Franz Boas (1858-1942) almost single-handedly established the current contours of anthropology, ridding it of all biological explanations for differences in human culture or behavior. Prof. MacDonald reports that he and his followers — with the notable exceptions of Margaret Meade and Ruth Benedict — were all Jews with strong Jewish identities: “Jewish identification and the pursuit of perceived Jewish interests, particularly in advocating an ideology of cultural pluralism as a model for Western societies, has been the ‘invisible subject’ of American anthropology.”
Franz Boas
By 1915, Boas and his students controlled the American Anthropological Association and by 1926 they headed every major American university anthropology department. From this position of dominance they promoted the idea that race and biology are trivial matters, and that environment counts for everything. They completely recast anthropology so as to provide intellectual support for open immigration, integration, and miscegenation. They also laid the foundation for the idea that because all races have the same potential, the failures of non-whites must be blamed exclusively on white oppression. The ultimate conclusion of Boasian anthropology was that since environment accounts for all human differences, every inequality in achievement can be eliminated by changing the environment. This has been the justification for enormous and wasteful government intervention programs.
The entire “civil rights movement” can be seen as a natural consequence of the triumph of Boasian thinking. Since all races were equivalent, separation was immoral. The color line also sharpened white self-consciousness in ways that might make whites more aware of Jewish parochialism. Thus it was, according to Prof. MacDonald, that Jews almost single-handedly launched the desegregation movement. Without the leadership of Jews, the NAACP might never have been established, and until 1975 every one of its presidents was a Jew. Prof. MacDonald reports that in 1917, when the black separatist Marcus Garvey visited NAACP headquarters, he saw so many white faces that he stormed out, complaining that it was a white organization.
Prof. MacDonald concludes that the efforts of Jews were crucial to the “civil rights” transformation of America. He quotes a lawyer for the American Jewish Congress who claims that “many of these [civil rights] laws were actually written in the offices of Jewish agencies by Jewish staff people, introduced by Jewish legislators and pressured into being by Jewish voters.”
While the Boas school was promoting integration and racial equivalence, it was also critical of, in Prof. Mac-Donald’s words, “American culture as overly homogeneous, hypocritical, emotionally and esthetically repressive (especially with regard to sexuality). Central to this program was creating ethnographies of idyllic [Third-World] cultures that were free of the negatively perceived traits that were attributed to Western culture.”
The role of the anthropologist became one of criticizing everything about Western society while glorifying everything primitive. Prof. MacDonald notes that Boasian portrayals of non-Western peoples deliberately ignored barbarism and cruelty or simply attributed it to contamination from the West. He sees this as a deliberate attempt to undermine the confidence of Western societies and to make them permeable to Third World influences and people. Today, this view is enshrined in the dogma that America must remain open to immigration because immigrants bring a spirit and energy that natives somehow lack.
Authoritarian Personalities
In order to open European-derived societies to the immigration that would transform them, it was necessary to discredit racial solidarity and commitment to tradition. Prof. MacDonald argues that this was the basic purpose of a group of intellectuals known as the Frankfurt School. What is properly known as the Institute of Social Research was founded in Frankfurt, Germany, during the Weimar period by a Jewish millionaire but was closed down by the Nazis shortly after they took power. Most of its staff emigrated to the United States and the institute reconstituted itself at UC Berkeley. The organization was headed by Max Horkheimer, and its most influential members were T.W. Adorno, Erich Fromm, and Herbert Marcuse, all of whom had strong Jewish identities. Horkheimer made no secret of the partisan nature of the institute’s activities: “Research would be able here to transform itself directly into propaganda,” he wrote. (Italics in the original)

Max Horkheimer and Theodor Adorno
Prof. MacDonald devotes many pages to an analysis of The Authoritarian Personality, which was written by Adorno and appeared in 1950. It was part of a series called Studies in Prejudice, produced by the Frankfurt school, which included titles like Anti-Semitism and Emotional Disorder. The Authoritarian Personality was particularly influential because, according to Prof. MacDonald, the American Jewish Committee heavily funded its promotion and because Jewish academics took up its message so enthusiastically.
The book’s purpose is to make every group affiliation sound as if it were a sign of mental disorder. Everything from patriotism to religion to family- and race-loyalty are signs of a dangerous and defective “authoritarian personality.” Because drawing distinctions between different groups is illegitimate, all group loyalties — even close family ties! — are “prejudice.” As Christopher Lasch has written, the book leads to the conclusion that prejudice “could be eradicated only by subjecting the American people to what amounted to collective psychotherapy — by treating them as inmates of an insane asylum.”
But according to Prof. MacDonald, it is precisely the kind of group loyalty, respect for tradition, and consciousness of differences central to Jewish identity that Horkheimer and Adorno described as mental illness in gentiles. These writers adopted what eventually became a favorite Soviet tactic against dissidents: Anyone whose political views were different from theirs was insane. As Prof. MacDonald explains, the Frankfurt school never criticized or even described Jewish group identity — only that of gentiles: “behavior that is critical to Judaism as a successful group evolutionary strategy is conceptualized as pathological in gentiles.”
For these Jewish intellectuals, anti-Semitism was also a sign of mental illness: They concluded that Christian self-denial and especially sexual repression caused hatred of Jews. The Frankfurt school was enthusiastic about psychoanalysis, according to which “Oedipal ambivalence toward the father and anal-sadistic relations in early childhood are the anti-Semite’s irrevocable inheritance.”
In addition to ridiculing patriotism and racial identity, the Frankfurt school glorified promiscuity and Bohemian poverty. Prof. MacDonald sees the school as a seminal influence: “Certainly many of the central attitudes of the largely successful 1960s countercultural revolution find expression in The Authoritarian Personality, including idealizing rebellion against parents, low-investment sexual relationships, and scorn for upward social mobility, social status, family pride, the Christian religion, and patriotism.”

Of greatest interest here, however, is the movement’s success in branding ancient loyalties to nation and race as mental illnesses. Although he came later, the French-Jewish “deconstructionist” Jacques Derrida was in the same tradition when he wrote:
The idea behind deconstruction is to deconstruct the workings of strong nation-states with powerful immigration polices, to deconstruct the rhetoric of nationalism, the politics of place, the metaphysics of native land and native tongue . . . The idea is to disarm the bombs . . . of identity that nation-states build to defend themselves against the stranger, against Jews and Arabs and immigrants . . .
As Prof. MacDonald puts it, “Viewed at its most abstract level, a fundamental agenda is thus to influence the European-derived peoples of the United States to view concern about their own demographic and cultural eclipse as irrational and as an indication of psychopathology.” Needless to say, this project has been successful; anyone opposed to the displacement of whites is routinely treated as a mentally unhinged “hate-monger,” and whenever whites defend their group interests they are described as psychologically inadequate. The irony has not escaped Prof. MacDonald: “The ideology that ethnocentrism was a form of psychopathology was promulgated by a group that over its long history had arguably been the most ethnocentric group among all the cultures of the world.”
Immigration

Prof. MacDonald argues that it is entirely natural for Jews to promote open immigration. It brings about the “diversity” Jews find comforting and it keeps America open to persecuted co-religionists throughout the world. He says Jews are the only group that has always fought for mass immigration; a few European ethnic organizations have made sporadic efforts to make it easier for their own people to come, but only Jews have consistently promoted open borders for all comers. Moreover, whatever disagreements they may have had on other issues, Jews of every political persuasion have favored high immigration.
This, too, goes back many years, and Prof. MacDonald traces in considerable detail the sustained Jewish pro-immigration effort. Israel Zangwill, author of the eponymous 1908 play The Melting Pot, was of the view that “[t]here is only one way to World Peace, and that is the absolute abolition of passports, visas, frontiers, custom houses . . .” He was nevertheless an ardent Zionist and disapproved of Jewish intermarriage.
Although the statue of liberty, properly known as Liberty Enlightening the World, was a gift to the United States from France as a tribute to American political traditions, the sonnet by the Jewish Emma Lazarus helped change it into a symbol of immigration. Affixed to the base of the statue several decades after its construction, the poem welcomes to America “huddled masses yearning to breath free /The wretched refuse of your teeming shore.”
Prof. MacDonald has discovered that implausible arguments about diversity being a quintessentially American strength have been made by Jews for a long time. He reports that in 1948 the American Jewish Committee was urging Congress to believe that “Americanism is the spirit behind the welcome that America has traditionally extended to people of all races, all religions, all nationalities.” Of course, there had never been such a tradition. In 1952, the American Jewish Congress argued in hearings on immigration that “our national experience has confirmed beyond a doubt that our very strength lies in the diversity of our peoples.” This, too, was at a time when U.S. immigration law was still explicitly designed to maintain a white majority.
It has often been said that when the old immigration policy was scrapped in 1965, scarcely anyone knew, and no one predicted, that the new law would change the racial makeup of the country. Prof. MacDonald disputes this, arguing that this had been the objective of Jewish groups from the beginning.
Prof. MacDonald finds that Jews have been the foremost advocates of immigration in England, France, and Canada, and that Jewish groups were the most vocal opponents of independence for Quebec. Australian Jews led the effort to dismantle the “white Australia” policy, one reason for which was cited in an editorial in the Australian Jewish Democrat: “The strengthening of multi-cultural or diverse Australia is also our most effective insurance policy against anti-Semitism. The day Australia has a Chinese Australian Governor General I would feel more confident of my freedom to live as a Jewish Australian.” Like Earl Raab writing about the United States, this Australian Jew is prepared to sacrifice the traditional culture, people, and identity of Australia to specifically Jewish interests. It would not be surprising if such an openly expressed objective did not have the opposite effect from that intended, and increase anti-Jewish sentiment.
Jews and the Left

It is well known that Jews have been traditionally associated with the left, and Prof. MacDonald investigates this connection in some detail. Historically it was understandable that Jews should support movements that advocated overthrowing the existing order. After emancipation, Jews met resistance from gentile elites who did not want to lose ground to competitors, and outsiders easily become revolutionaries. However, in Prof. MacDonald’s view, Jewish commitment to leftist causes has often been motivated by the hope that Communism, especially, would be a tool for combating anti-Semitism, and by the expectation that universalist social solutions would be yet another way to dissolve gentile loyalties that might exclude Jews. The appeal of universalist ideologies is tied to the implicit understanding that Jewish particularism will be exempt: “At the extreme, acceptance of a universalist ideology by gentiles would result in gentiles not perceiving Jews as in a different social category at all, while nonetheless Jews would be able to maintain a strong personal identity as Jews.”
Prof. MacDonald argues that Jews had specifically Jewish reasons for supporting the Bolshevik revolution. Czarist Russia was notorious for its anti-Semitic policies and, during its early years, the Soviet Union seemed to be the promised land for Jews: it ended state anti-Semitism, tried to eradicate Christianity, opened opportunities to individual Jews, and preached a “classless” society in which Jewishness would presumably attract no negative attention.Moreover, since Marxism taught that all conflict was economic rather than ethnic, many Jews believed it heralded the end of anti-Semitism.
Prof. MacDonald emphasizes that although Jewish Communists preached both atheism and the solidarity of the world’s working people, they took pains to preserve a distinct, secular Jewish identity. He reports that Lenin himself (who had one Jewish grandparent) approved the continuation of an explicitly Jewish identity under Communism, and in 1946 the Communist Party of the United States voted a resolution also supporting Jewish peoplehood in Communist countries. Thus, although Communism was supposed to be without borders or religion, Jews were confident that it would make a place for their own group identity. He writes that despite the official view that all men were to be brothers, “very few Jews lost their Jewish identity during the entire Soviet era.”
Jewish Communists sometimes betrayed remarkable particularism. Prof. MacDonald quotes Charles Rappoport, the French Communist leader: “The Jewish people [are] the bearer of all the great ideas of unity and human community in history . . . The disappearance of the Jewish people would signify the death of humankind, the final transformation of man into a wild beast.” This seems to attribute to Jews an elite position incompatible with “unity and human community.”
Prof. MacDonald argues that many Jews began to fall away from Communism only after Stalin showed himself to be anti-Semitic. And just as Jews had been the leading revolutionaries in anti-Semitic pre-Revolutionary Russia, Jews became the leading dissidents in an anti-Semitic Soviet Union. A similar pattern can be found in the imposed Communist governments of Eastern Europe, which were largely dominated by Jews. The majority of the leaders of the Polish Communist Party, for example, spoke better Yiddish than Polish, and they too maintained a strong Jewish identity. After the fall of Communism many stopped being Polish and emigrated to Israel.

Prof. MacDonald writes that in Bela Kun’s short-lived 1919 Communist government of Hungary, 95 percent of the leaders were Jews, and that at the time of the 1956 uprising Communism was so closely associated with Jews that the rioting had almost the flavor of a pogrom. He argues that in the United States as well, the hard core among Communists and members of Students for a Democratic Society (SDS) was mainly Jewish. Here, too, a revolutionary, atheist, and universalist world-view was fully compatible with strong identification as Jews. Prof. MacDonald quotes from a study of American leftists:
Many Communists, for example, state that they could never have married a spouse who was not a leftist. When Jews were asked if they could have married Gentiles, many hesitated, surprised by the question, and found it difficult to answer. Upon reflection, many concluded that they had always taken marriage to someone Jewish for granted. Their commitment as Jews was even more fundamental and unexamined than their commitment to the left.
Prof. MacDonald reports that many American Jews also abandoned Communism as it became increasingly anti-Semitic. For a large number, the Soviet Union’s severing of diplomatic ties with Israel during the 1967 war was the last straw. A former SDS activist no doubt spoke for many when he explained, “If I must choose between the Jewish cause and a “progressive’ anti-Israel SDS, I shall choose the Jewish cause. If barricades are erected, I will fight as a Jew.” According to Prof. MacDonald, American neoconservatism can also be described as a surface shift in external politics that leaves the more fundamental commitment to Jewish identity unchanged. Thus, former leftists abandoned an ideology that had turned against Israel and refashioned American conservatism into a different movement, the one unshakable theme of which was support for Israel. Neoconservatives also support high levels of immigration and were active in excluding white racial identification from the “respectable” right.
Objections
There are many possible objections to Prof. MacDonald’s thesis. The first is that it is largely built on the assumption that Jews are dishonest. It is always risky to assume one understands the motives of others better than they do themselves. Jews have traditionally thought of themselves as a benevolent presence, even as a “light unto the nations” or a “chosen people.” This is echoed today in the Jewish self image as champions of the excluded and the oppressed. Most of the time what passes for “social justice” has the effect of undermining the traditions and loyalties of gentile society, but are Jews deliberately undermining these things rather than righting what they perceive to be wrongs?
Prof. MacDonald concedes that many Jews are sincere in their support for liberal causes, but then escalates his indictment by arguing that “the best deceivers are those who deceive themselves.” In other words, many Jews who are actually working for Jewish interests have first convinced themselves otherwise. A Jew who mainly wants America to become less white may also have convinced himself that America benefits from a multitude of cultures. Having convinced himself he can more effectively convince others.
Many Jews, Prof. MacDonald argues, are not even conscious of the extent to which their Jewishness is central to their identities or their political views. He quotes Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel on his surprise at how passionately he embraced the Israeli side during the 1967 war: “I had not known how Jewish I was.” This is an arresting statement from a man who was thought to be perhaps the greatest Jewish spiritual leader of his time. And whether or not it affects their politics, Jews certainly appear to have a very vivid sense of peoplehood. Prof. MacDonald quotes theologian Eugene Borowitz as saying, “most Jews claim to be equipped with an interpersonal friend-or-foe sensing device that enables them to detect the presence of another Jew, despite heavy camouflage.” Always to think in terms of “friend or foe” is no insignificant matter.

Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel (Credit Image: Peter1c / Wikimedia)
Prof. MacDonald is therefore skeptical of Jewish disavowals: “Surface declarations of a lack of Jewish identity may be highly misleading.” He notes that Jewish publications write about the power and influence of American Jews in language Jews would immediately denounce as “anti-Semitic” if used by gentiles. He agrees with Joseph Sobran, who has said “they want to be Jews among themselves but resent being seen as Jews by Gentiles. They want to pursue their own distinct interests while pretending that they have no such interests . . .”
Prof. MacDonald argues that the success of Jewish-led intellectual movements has been possible only because their Jewish character was hidden. If multiculturalism or mass immigration or The Authoritarian Personality had been promoted by Orthodox Jews in black coats the Jewish element would have been clear. Prof. MacDonald writes that in fact, “the Jewish political agenda was not an aspect of the theory and the theories themselves had no overt Jewish content. Gentile intellectuals approaching these theories were therefore unlikely to view them as aspects of Jewish-gentile cultural competition or as an aspect of a specifically Jewish political agenda.” Prof. MacDonald also claims that Jews have often tried to conceal the Jewish character of an intellectual movement by recruiting token gentiles for visible positions as spokesmen. He writes that this tactic was so common in the American Communist Party that gentiles often saw through it and resigned.
But how can motives ever be completely known? Prof. MacDonald sets a difficult test: “The best evidence that individuals have really ceased to have a Jewish identity is if they choose a political option that they perceive as clearly not in the interests of Jews as a group. In the absence of a clearly perceived conflict with Jewish interests, it remains possible that different political choices among ethnic Jews are only differences in tactics for how best to achieve Jewish interests.”
This standard may seem unduly harsh — until it is applied to white gentiles. Third-World immigration, affirmative action, anti-discrimination laws, and forced integration are clearly not in the interests of whites, yet many whites embrace them, thus demonstrating how completely they have abandoned their racial identity.
Finally, Prof. MacDonald raises the disturbing possibility that some Jews, because of centuries of conflict with gentiles, actively hate gentile society and consciously wish to destroy it: “a fundamental motivation of Jewish intellectuals involved in social criticism has simply been hatred of the gentile-dominated power structure perceived as anti-Semitic.” He describes the 19th century German-Jewish poet Heinrich Heine as “using his skill, reputation and popularity to undermine the intellectual confidence of the established order.”
In defense of this highly provocative view, Prof. MacDonald quotes Benjamin Disraeli on the effects of centuries of Jewish-gentile relations on Jews: “They may have become so odious and so hostile to mankind as to merit for their present conduct, no matter how occasioned, the obloquy and ill-treatment of the communities in which they dwell and with which they are scarcely permitted to mingle.”
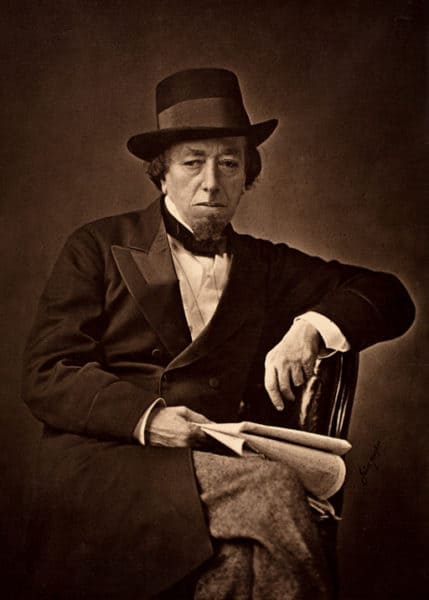

Benjamin Disraeli
Apart from any question of motives, however, is the question of numbers. Jews are a tiny minority in the United States and within that minority there is disagreement even on matters that clearly affect Jews. How can Jews possibly be responsible for dramatic changes in the intellectual landscape? In Prof. MacDonald’s view, the explanation lies in the intelligence, energy, dedication, and cohesiveness of Jews. He attributes a great deal to the average IQ of Jews — at 115, a full standard deviation above the white gentile average — and to “their hard work and dedication, their desire to make a mark on the world, and their desire to rise in the world, engage in personal promotion, and achieve public acclaim . . .” He also believes Jews have worked together unfailingly on any question they considered necessary for survival: “Intellectual activity is like any other human endeavor: Cohesive groups outcompete individualist strategies.” He notes that there has never been a time when large numbers of white Americans favored non-white immigration; it was a cohesive, determined minority that beat down the disorganized resistance of the majority.
Prof. MacDonald believes that because of the effectiveness of some Jews, it was not even necessary that most Jews actively support anti-majoritarian movements, but that Jewish activity was still decisive. As he puts it, “Jewish-dominated intellectual movements were a critical factor (necessary condition) for the triumph of the intellectual left in late twentieth-century Western societies.” This, of course, can never be tested, but there can be no doubt that American Jews have had a disproportionate effect on the American intellect. Prof. MacDonald quotes Walter Kerr, writing in 1968, to the effect that “what has happened since World War II is that the American sensibility has become part Jewish, perhaps as much Jewish as it is anything else . . . The literate American mind has come in some measure to think Jewishly.”
Aside from the question of whether Prof. MacDonald is right is the further question of what difference it makes if he is right. If correct, his thesis certainly sheds light on the rapidity with which whites lost their will. Just a few decades ago whites were a confident race, proud of their achievements, convinced of their fitness to dominate the globe. Today they are a declining, apologetic people, ashamed of their history and not sure even of their claim to lands they have occupied for centuries. It is very rare for fundamental concepts to be stood on their heads in the course of just a generation or two, as has happened with thinking about race. Such speed suggests there has been something more than natural change.
And yet, as is clear just from the articles that appear in American Renaissance, Jewish intellectuals are by no means unanimous in denying the importance of race. Jews are present in the foremost ranks of those who would reintegrate biology into the social sciences, stop Third-World immigration, and halt government interference in race relations. If Jews have undermined the traditions on which Western Civilization depends, so are they now undermining the liberal orthodoxy that continues to threaten those traditions.
There can be no doubting the energy and influence of this remarkable people. It would be foolish and ungrateful not to recognize that this energy and influence can help save what is left of a beleaguered civilization.















