Millions of Poor Are Left Uncovered by Health Law
Sabrina Tavernise and Robert Gebeloff, New York Times, October 3, 2013
A sweeping national effort to extend health coverage to millions of Americans will leave out two-thirds of the poor blacks and single mothers and more than half of the low-wage workers who do not have insurance, the very kinds of people that the program was intended to help, according to an analysis of census data by The New York Times.
Because they live in states largely controlled by Republicans that have declined to participate in a vast expansion of Medicaid, the medical insurance program for the poor, they are among the eight million Americans who are impoverished, uninsured and ineligible for help. The federal government will pay for the expansion through 2016 and no less than 90 percent of costs in later years.
Those excluded will be stranded without insurance, stuck between people with slightly higher incomes who will qualify for federal subsidies on the new health exchanges that went live this week, and those who are poor enough to qualify for Medicaid in its current form, which has income ceilings as low as $11 a day in some states.
{snip}
The 26 states that have rejected the Medicaid expansion are home to about half of the country’s population, but about 68 percent of poor, uninsured blacks and single mothers. About 60 percent of the country’s uninsured working poor are in those states. Among those excluded are about 435,000 cashiers, 341,000 cooks and 253,000 nurses’ aides.
{snip}
The disproportionate impact on poor blacks introduces the prickly issue of race into the already politically charged atmosphere around the health care law. Race was rarely, if ever, mentioned in the state-level debates about the Medicaid expansion. But the issue courses just below the surface, civil rights leaders say, pointing to the pattern of exclusion.
Every state in the Deep South, with the exception of Arkansas, has rejected the expansion. Opponents of the expansion say they are against it on exclusively economic grounds, and that the demographics of the South — with its large share of poor blacks — make it easy to say race is an issue when it is not.
In Mississippi, Republican leaders note that a large share of people in the state are on Medicaid already, and that, with an expansion, about a third of the state would have been insured through the program. Even supporters of the health law say that eventually covering 10 percent of that cost would have been onerous for a predominantly rural state with a modest tax base.
{snip}
The law was written to require all Americans to have health coverage. For lower and middle-income earners, there are subsidies on the new health exchanges to help them afford insurance. An expanded Medicaid program was intended to cover the poorest. In all, about 30 million uninsured Americans were to have become eligible for financial help.
But the Supreme Court’s ruling on the health care law last year, while upholding it, allowed states to choose whether to expand Medicaid. Those that opted not to leave about eight million uninsured people who live in poverty ($19,530 for a family of three) without any assistance at all.
{snip}
About half of poor and uninsured Hispanics live in states that are expanding Medicaid. But Texas, which has a large Hispanic population, rejected the expansion. {snip}
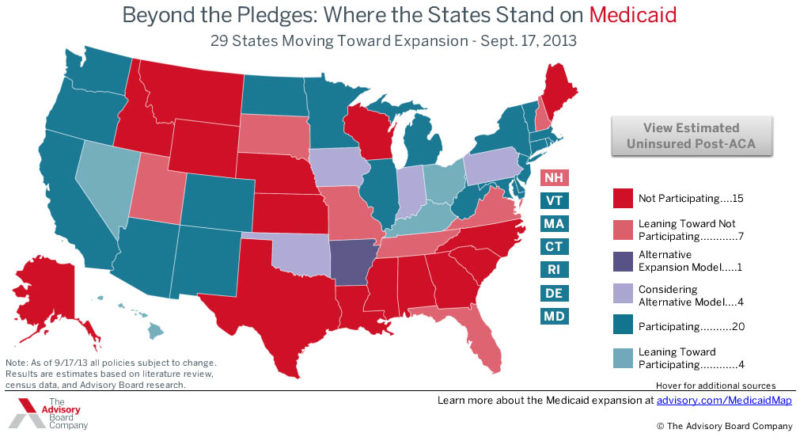
[Editor’s Note: The map below shows each state’s position on Medicaid expansion.]